High availability (HA) is the ability to make our application continuously operational without any failures. By configuring Pod Anti-affinity and Pod disruption budget together will make stateful or stateless application pods to highly available during any of the below scenarios:
- Any one/many nodes is unavailable or under maintenance
- Cluster administrator deletes Kubernetes nodes by mistake
- Cluster administrator/User deletes your application pods by mistake
In this blog, We are going to configure both pod anti-affinity and Pod disruption budget for the kubernetes deployment
Pod Anti-affinity:
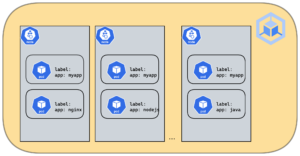
Pod Anti-affinity: It help us not to schedule same type of pod in one node which means you will have only one pod in one node and other same type pod in another node. Hence scheduler will never co-locate the same type of pod in the same node
For Example, if three pods of same deployment(replicas=3) are in one node and that node has crashed or unavailable, then our application will be impacted. When pod anti-affinity is configured, one node failure/unavailable will not impact the whole application.
1) Configure the below snippet under template.spec in the application deployment yaml
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- myapp
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
Note: Pod Antiaffinity uses Selector to match with key:app in value:myapp and uses node labels
2) Sample deployment yaml with pod anti-affinity:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp
labels:
apptype: java
app: myapp
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
apptype: java
template:
metadata:
labels:
apptype: java
app: myapp
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- myapp
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
containers:
- name: container-name
image: [Application GCR image]
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["java -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/var/log/my-heap-dump.hprof -Xloggc:/var/log/myAppgc.log -jar [application.jar] --spring.config.location=[absolute path of the config map eg. /config/application/[application.properties]] "]
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
volumeMounts:
- name: appconfig
mountPath: "/config/application"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: appconfig
configMap:
name: [configmap-name]
3) Save the above mentioned deployment yaml and deploy it in kubernetes cluster by executing the below command
kubectl apply -y [deployment.yaml]
Pod Disruption Budget:
Pod Disruption Budget help us to define how many minimum available and maximum unavailable pods must meet the condition even during disruption for stateful or stateless application. You can define minAvailable/maxUnavailable values either as integer or percentage.
You can configure Pod disruption budget in two ways or both:
1) minAvailable – Specified value/percentage of pod should be available always
cat > pdbmin.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: policy/v1
kind: PodDisruptionBudget
metadata:
name: pdb-myapp
spec:
maxUnavailable: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
EOF
2) maxUnavailable – Specified value/percentage of pod can be acceptable during disruption
cat > pdbmax.yaml << EOF
apiVersion: policy/v1
kind: PodDisruptionBudget
metadata:
name: pdb2-myapp
spec:
minAvailable: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
EOF
Note: minAvailable and maxUnavailable cannot be both set in a single yaml. You need to create two pod disruption budget if you are configuring both minAvailable and maxUnavailable for your application deployment
3) We have already deployed our application with label app: myapp. To configure pod disruption budget, save the above two PodDisruptionBudget yamls and deploy it in the kubernetes cluster by executing the below commands:
kubectl apply -f pdbmin.yaml kubectl apply -f pdbmax.yaml
Note: Now Pod Disruption Budget is applied for the label app: myapp
4) Verify the pod disruption budgets by executing the below command:
kubectl get pdb
Conclusion:
End of the day, Application needs to be highly available in production. Pod Anti-affinity and Pod Disruption Budget together will make the application run without zero downtime.